Document Q&A
This guide will help you build a Document Q&A app with step-by-step instructions, using Data Sources.
Make sure you're signed up on Dust and have reviewed the Quickstart guide.
This document assumes that you know how to create a Dust app and that you have already set up OpenAI as a provider on your account. If you haven't done so, please refer to our Quickstart guide for step-by-step instructions.
In this guide we will use a Data Source to store and index a set of documents and make their content available to a large language model using semantic search in order to answer questions about them.
The main limitation of LLMs when it comes to answering questions about long documents is that the documents cannot fit in the LLM context size. Data sources allow us to overcome this limitation by splitting documents into smaller chunks and indexing these chunks separately.
Given a question, we can then use semantic search to find the most relevant chunks relative to the question and feed these chunks to a LLM to generate an answer.
Creating your first Data Source
We will use a Data Source to automatically chunk, embed and index 4 IPCC reports: AR6-WG1, AR6-WG2, AR6-WG3 and AR6-SYR.
You can create your first Data Source from your Dust home page by selecting the Data Sources tab
and clicking on the New DataSource button. You'll need to provide a name and description as well
as select OpenAI's embedding model text-embedding-ada-002. Finally, it is important to pick a
max_chunk_size value. We decided to use max_chunk_size=256 for this example (in tokens), to be
able to insert 12 chunks in-context and leave 1024 tokens for generating an answer as we plan to use
gpt-3.5-turbo which has a context size of 4096 tokens.
Increasing the max_chunk_size would provide more context per chunk but would also reduce the
number of chunks the model can attend to in-context. Reducing it would allow to consider more
"sources" of information but would reduce the amount of information captured by each chunk. 256
tokens appears like a good trade-off for here but the right value will depend on your
use case and the model you use (as an example, gpt-4 has 8192 tokens of context, so we could use a
max_chunk_size of 512).
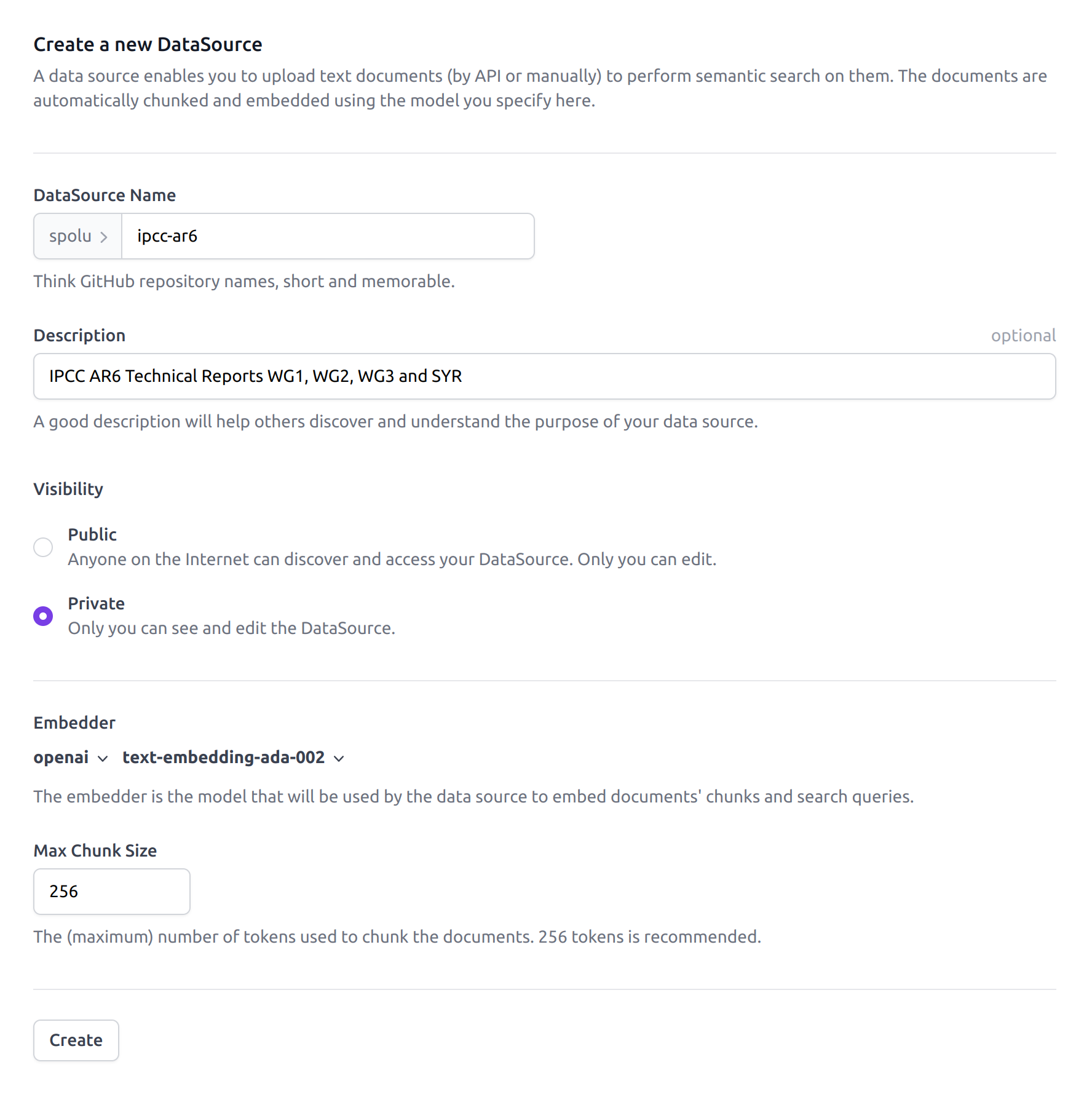
The Dust Data Source creation panel. The name should be short and
memorable, lowercase without spaces.
Inserting documents
Once the Data Source is created, you can click on Upload Document to insert documents from the interface. Note that it is also possible to insert Documents by API.
When inserting a Document, a unique document identifier needs to be provided. Free form tags (on
which semantic search can be filtered) can also be provided. Text content is filled automatically
here by uploading the text format of a local ipcc_ar6_wg1.txt file which was obtained by
extracting the text of the associated IPCC PDFs. Insertion acts as an upsert, updating the document
if it already existed for the provided identifier.
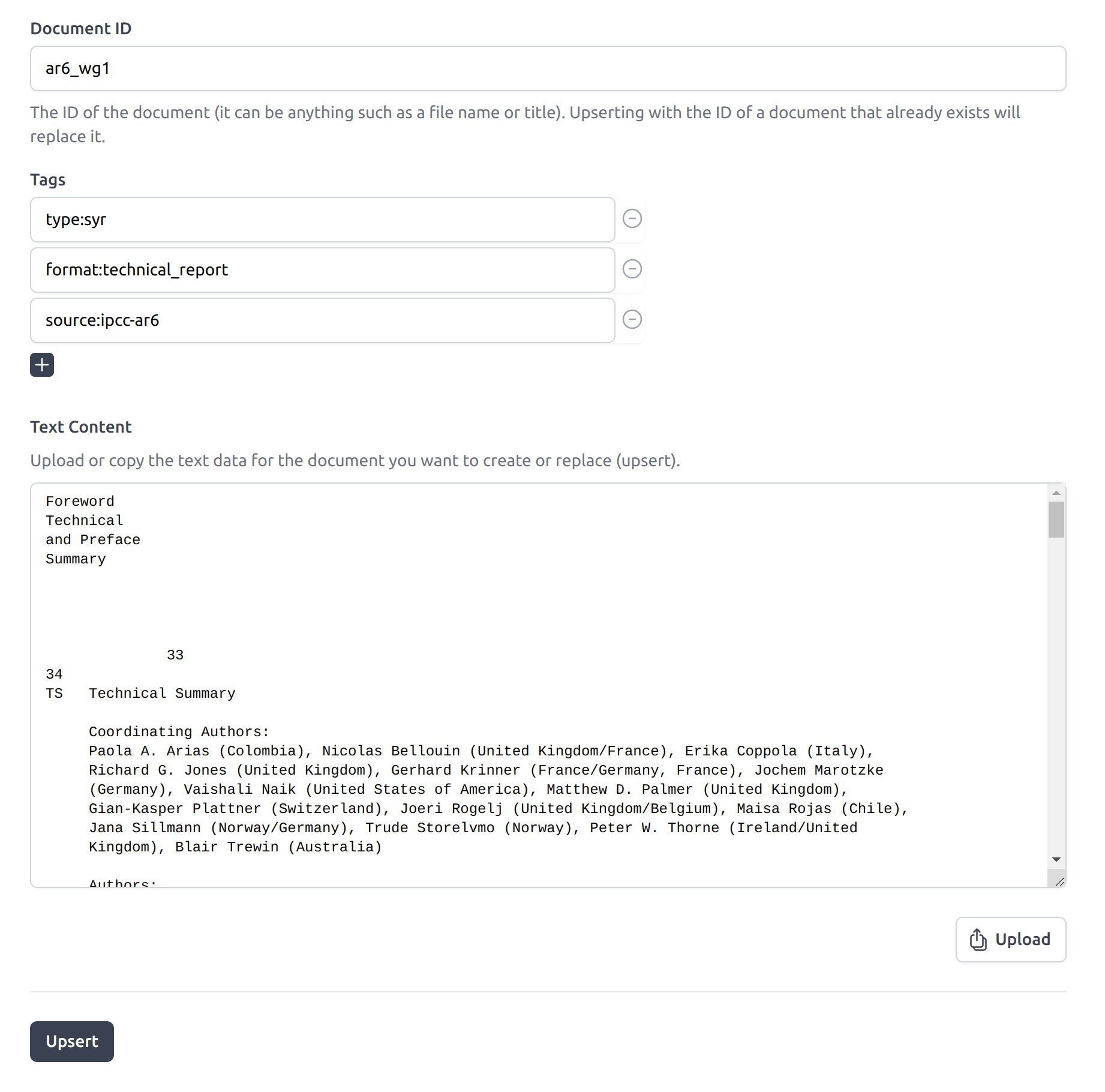
The Dust Data Source document insertion interface. Tags are optional and arbitrary. The text content was filled here using the Upload button.
Once the 4 documents are inserted, you should be able to see them in the Data Source interface. You can review the public ipcc-ar6 Data Source as an example.
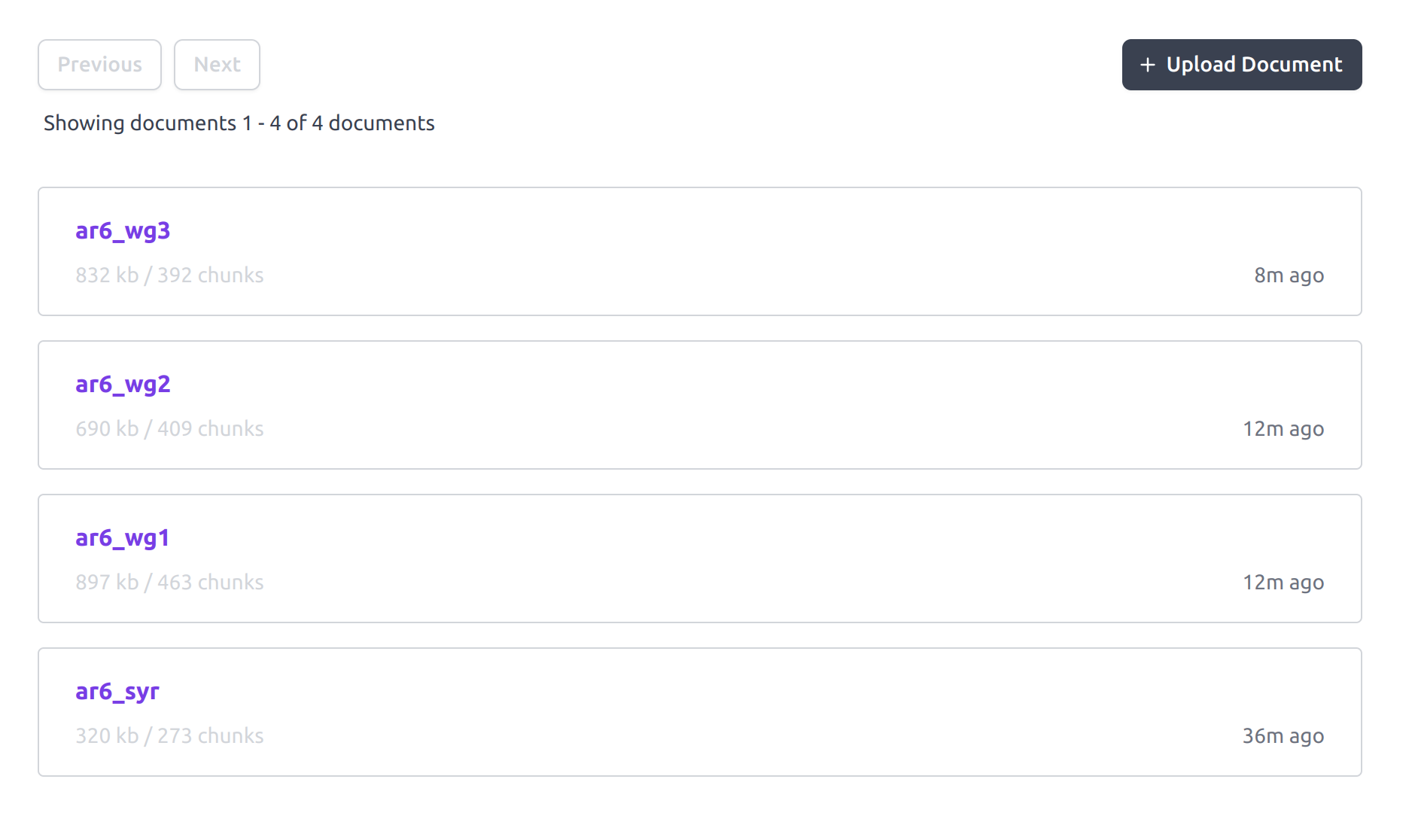
The Dust Data Source documents list. You can inspect and edit each of the document from this interface. The size of each document and the resulting number of chunks that were created, embedded and indexed is also reported.
Now that your Data Source is ready, you can move on to the next section to create a Q&A app that will use it.
Creating a Q&A app
In this section we'll provide step-by-step instructions to create a Q&A app that will use the data source to answer user-provided questions.
input block
From your home screen create a new app by clicking the Apps tab and then the New App button.
Assuming you've already covered our Quickstart guide, add an input block and associate it with a new dataset with a few questions that might be relevant to the Data Source:
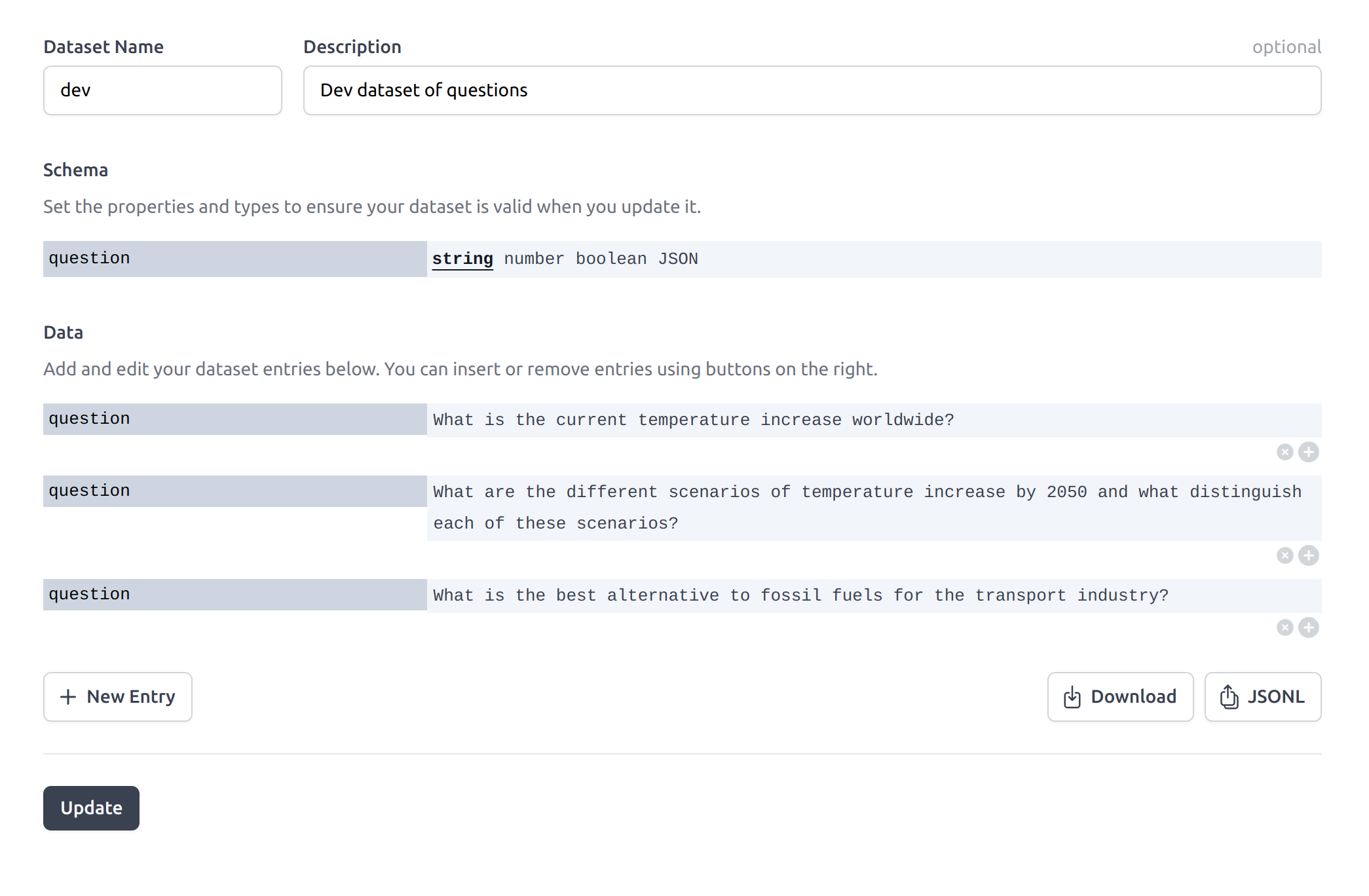
An example dataset with questions relative to the Data Source we plan to use. Each question is a different input against which we will design our app.
data_source block
Once the input block points to your new dataset you can add a data_source block and select your
Data Source. If you want to use the publicly available Data Source
ipcc-ar6, edit the user name to spolu and then select
ipcc-ar6. You should set top_k to 12, meaning that we'll consume 3072 tokens of context to
present chunks to the model.
The query can be set directly to the question from the input using templating with the following value:
{{INPUT.question}}
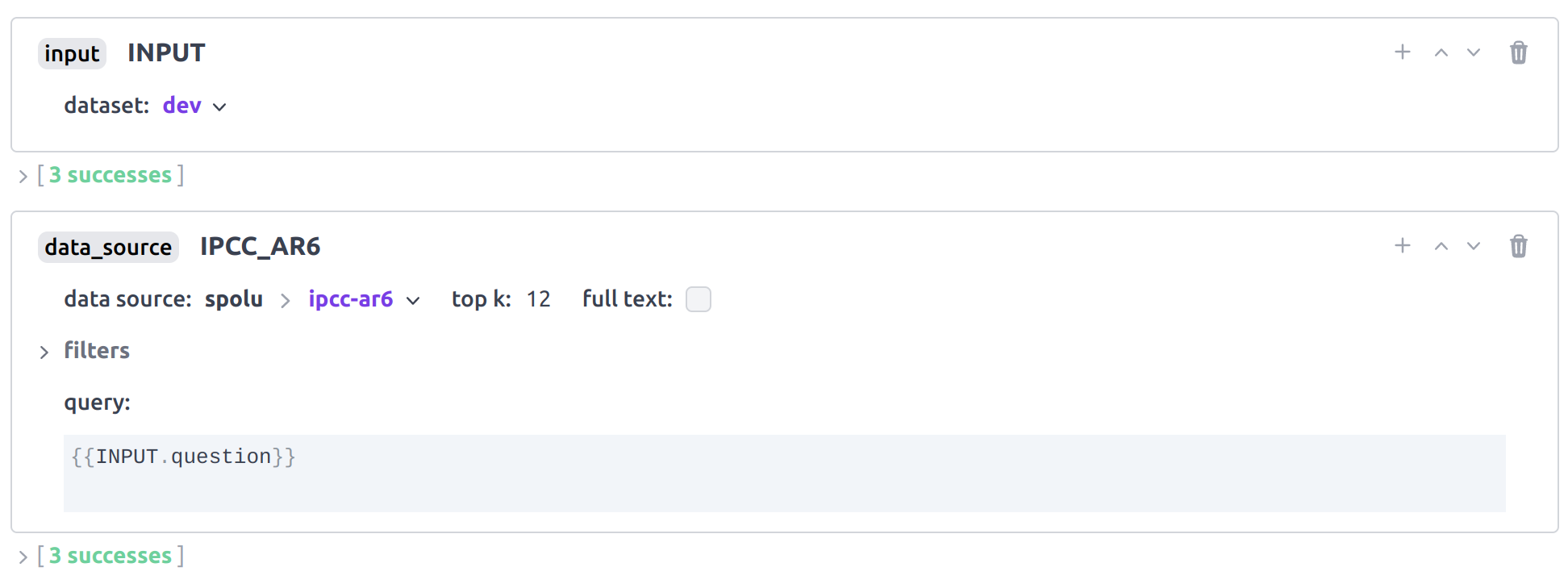
The Dust data_source block pointing to the ipcc-ar6 Data Source. The
query is set to the input value question field using templating.
At this point you can run your app and introspect the outputs of the data_source block.
chat block
We will use gpt-3.5-turbo to process the chunks and generate an answer to the user.
We use the following instruction in the context of ipcc-ar6:
You are an helpful assistant. For each user question, you'll receive 12 additional system
messages with chunks of text retrieved by semantic search (based on the question) from IPCC
AR6 technical reports SYR, WG1, WG2, and WG3. You should reply to the user with a concise
but precise answer that is only based on the chunks of text that were presented to you.
And the following code to construct the set of messages presented to the model:
_fun = (env) => {
let messages = [{ role: "user", content: env.state.INPUT.question }];
env.state.IPCC_AR6.forEach((d) => {
d.chunks.forEach((c) => {
messages.push({
role: "system",
content: `From: ${d.document_id}\n\n${c.text}`,
});
});
});
return messages;
};
final code block
To return only the content generated by the model you can add a final code block with the following code:
_fun = (env) => {
return env.state.MODEL.message.content;
};
You can now run your app and inspect the outputs of the last code block.
Using the app
You can use the Use tab to submit new questions to your app and get generated answers direclty.
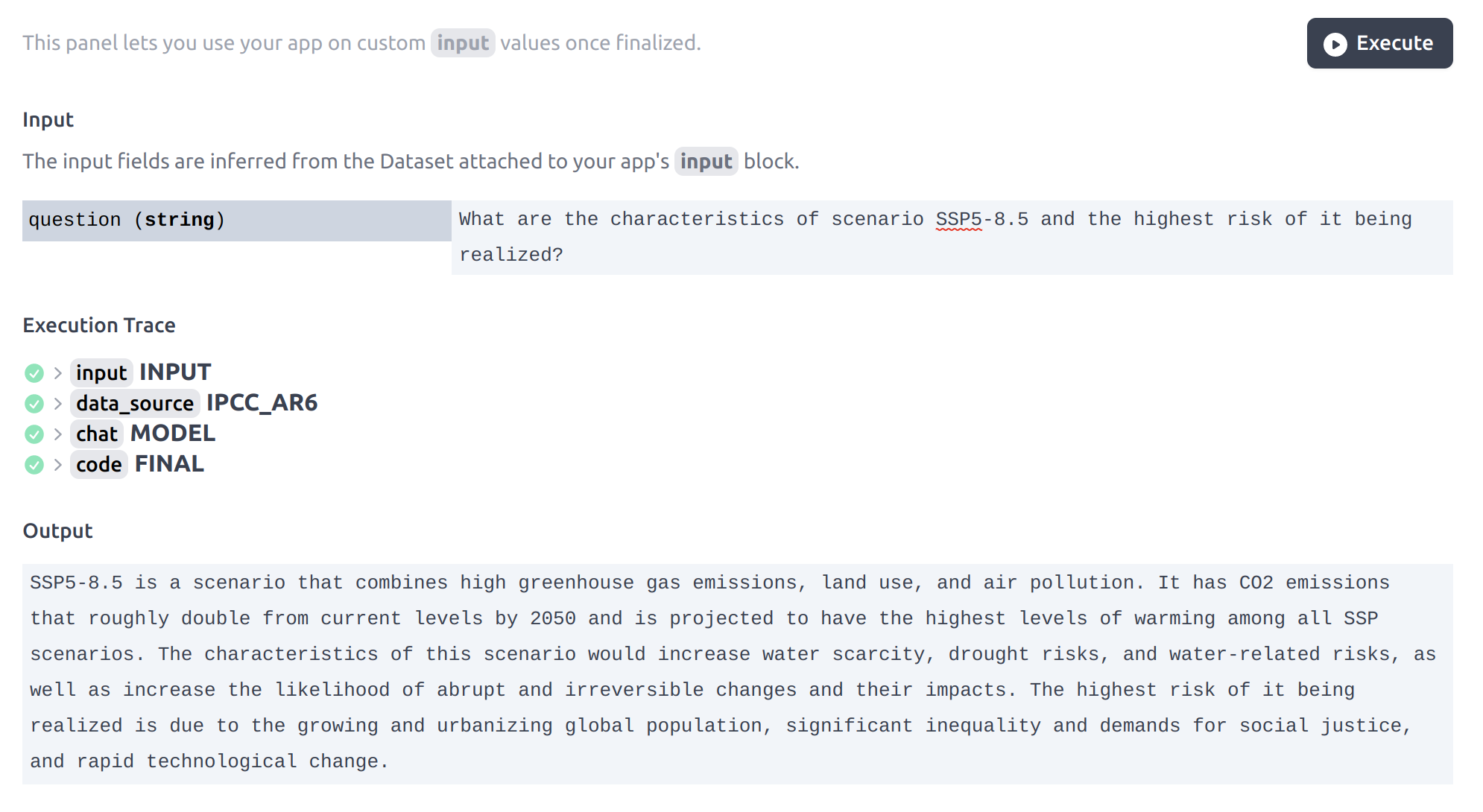
The app Use interface. You can submit new questions and get generated answers directly.